Supercharging LED technology
with chirality
RADIANT produces efficient, affordable and sustainable chiral LEDs

LEDs: Huge market potential, increasing sustainability concerns
Need for innovations to reduce the carbon footprint of LEDs
LEDs (light-emitting diodes) are energy-efficient light-source technologies used widely in diverse applications, such as lighting, digital displays, and optical communications. Given the continuously increasing consumption of energy and the dominance of LEDs for illumination, their market is expected to grow to more than 193 billion dollars by 2030.

However, LED production currently depends on critical raw materials like Arsenic (As), Gallium (Ga), and Germanium (Ge). Our project RADIANT aims to produce LEDs more sustainably by enhancing the properties of alternative LED technologies through novel nanoimprinting that implements chirality.
Chirality:
A cost-effective solution to improve LED performance
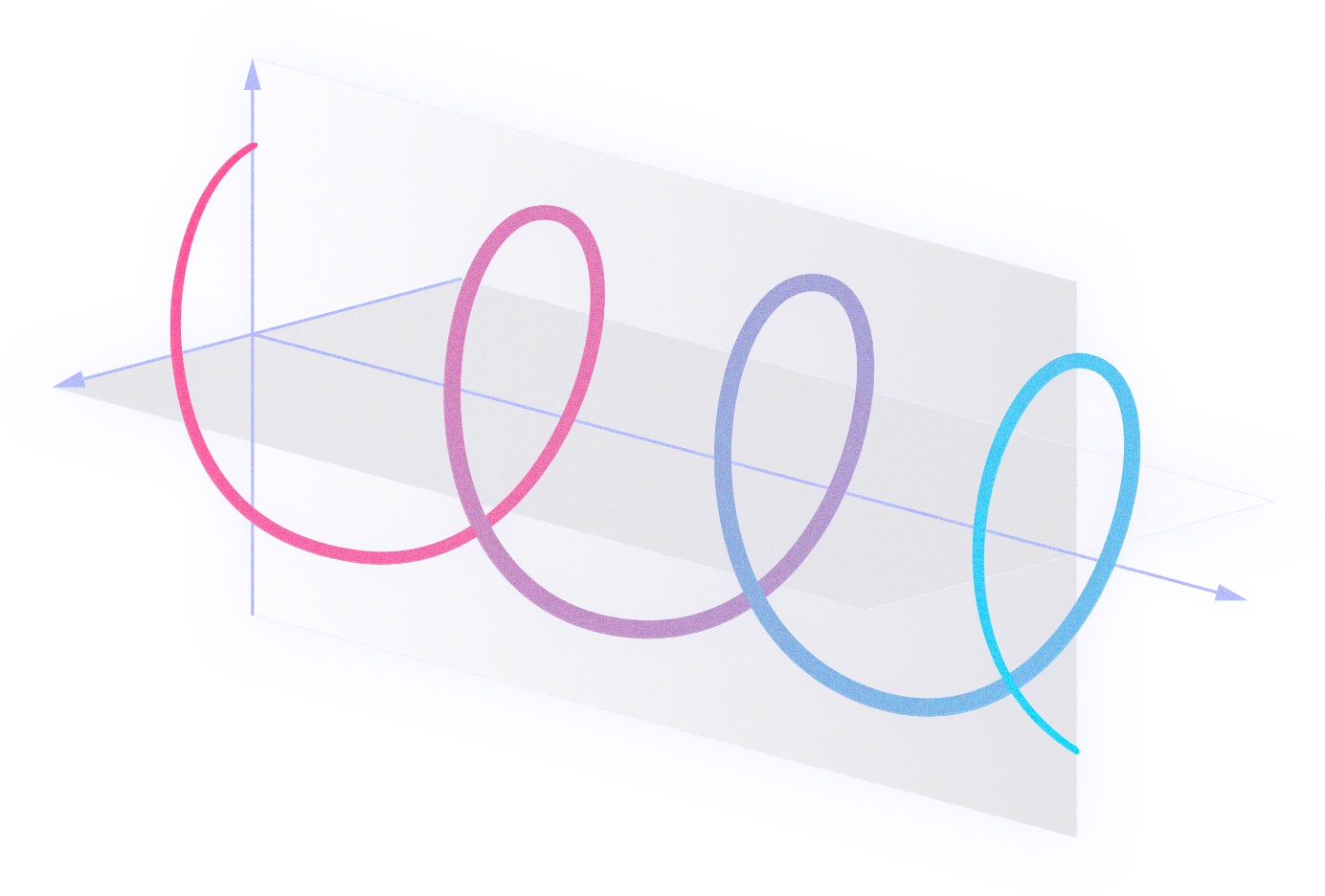
While these types of photonic nanostructures tend to be expensive and difficult to scale up, in RADIANT, we develop them using affordable, sustainable, and scalable soft nanoimprinting lithography.
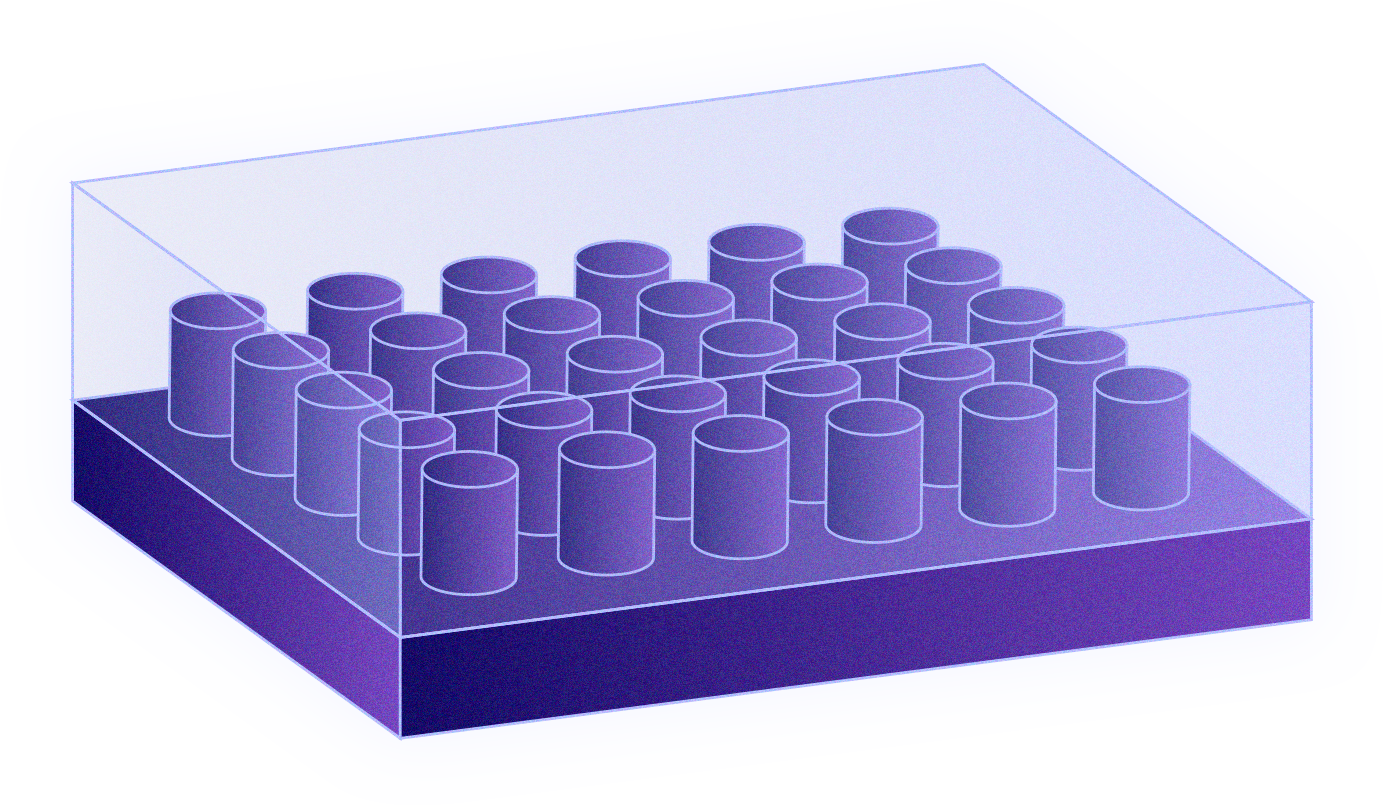
The RADIANT approach:
New generation of chiral LEDs
Enhanced optical properties, less burden on the environment
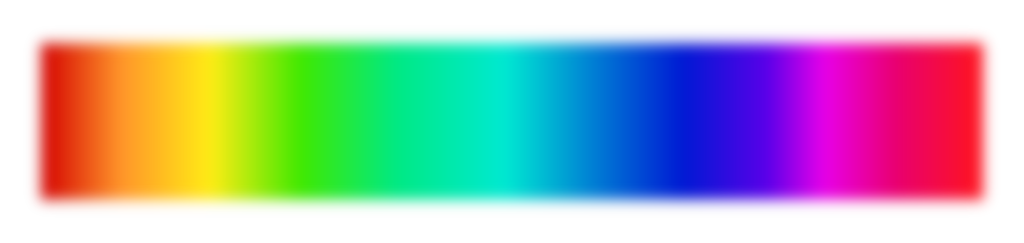
The spectral range of chiral LEDs is very broad, ranging from the visible to the near-infrared invisible to the human eye. This opens possibilities for using chiral LEDs in various fields, including display technology, medical imaging, remote sensing, and optical communications.
With our approach, we intend to revolutionise the lighting and illumination industry by improving LEDs’ efficiency and providing exceptionally bright output, while simultaneously reducing production costs and curbing their environmental impact.


This Project has received funding from the European Union Horizon Europe Research and Innovation program under grant agreement Nº 101162112
Follow us!
